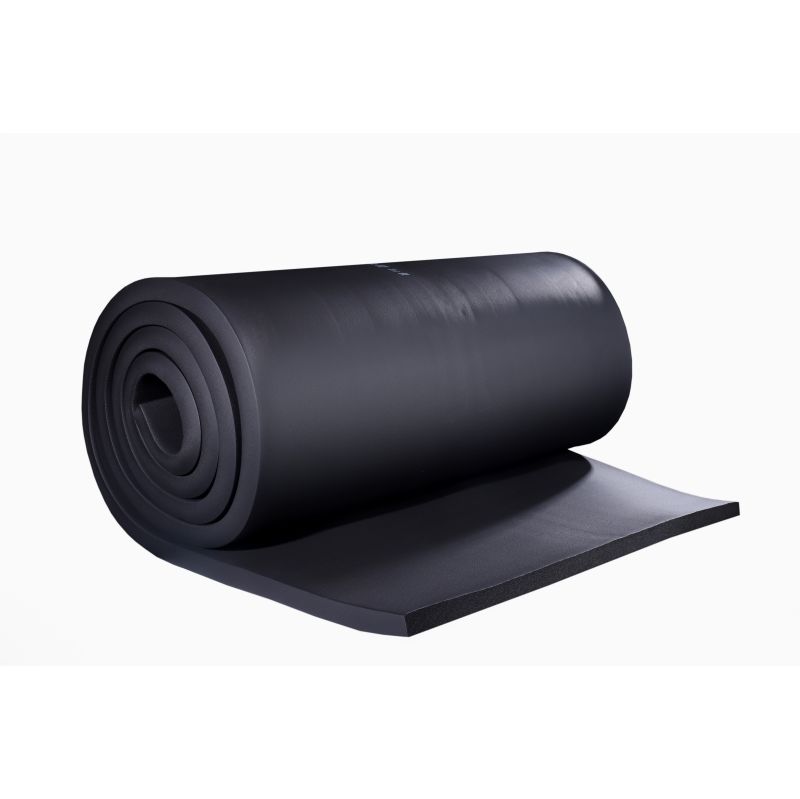
Kingflex Thermal Insulation Rubber Foam Sheet
Description
The expanded closed-cell structure makes it an efficient insulation. It is manufactured without the use of CFC's, HFC's or HCFC's. Kingflex Thermal Insulation Rubber Foam Sheet is also effective for reducing HVAC noise. On cold systems, insulation thicknesses have been calculated to control condensation on the insulation outer surface, as shown in the table of thickness recommendation.
Standard Dimension
|
Kingflex Dimension |
|||||||
|
Thickness |
Width 1m |
Width 1.2m |
Width 1.5m |
||||
|
Inches |
mm |
Size(L*W) |
㎡/Roll |
Size(L*W) |
㎡/Roll |
Size(L*W) |
㎡/Roll |
|
1/4" |
6 |
30 × 1 |
30 |
30 × 1.2 |
36 |
30 × 1.5 |
45 |
|
3/8" |
10 |
20 × 1 |
20 |
20 × 1.2 |
24 |
20 × 1.5 |
30 |
|
1/2" |
13 |
15 × 1 |
15 |
15 × 1.2 |
18 |
15 × 1.5 |
22.5 |
|
3/4" |
19 |
10 × 1 |
10 |
10 × 1.2 |
12 |
10 × 1.5 |
15 |
|
1" |
25 |
8 × 1 |
8 |
8 × 1.2 |
9.6 |
8 × 1.5 |
12 |
|
1 1/4" |
32 |
6 × 1 |
6 |
6 × 1.2 |
7.2 |
6 × 1.5 |
9 |
|
1 1/2" |
40 |
5 × 1 |
5 |
5 × 1.2 |
6 |
5 × 1.5 |
7.5 |
|
2" |
50 |
4 × 1 |
4 |
4 × 1.2 |
4.8 |
4 × 1.5 |
6 |
Technical Data Sheet
|
Kingflex Technical Data |
|||
|
Property |
Unit |
Value |
Test Method |
|
Temperature range |
°C |
(-50 - 110) |
GB/T 17794-1999 |
|
Density range |
Kg/m3 |
45-65Kg/m3 |
ASTM D1667 |
|
Water vapor permeability |
Kg/(m.s.pa) |
≤0.91×10 ﹣¹³ |
DIN 52 615 BS 4370 Part 2 1973 |
|
μ |
- |
≥10000 |
|
|
Thermal Conductivity |
W/(m.k) |
≤0.030 (-20°C) |
ASTM C 518 |
|
≤0.032 (0°C) |
|||
|
≤0.036 (40°C) |
|||
|
Fire Rating |
- |
Class 0 & Class 1 |
BS 476 Part 6 part 7 |
|
Flame Spread and Smoke Developed Index |
|
25/50 |
ASTM E 84 |
|
Oxygen Index |
|
≥36 |
GB/T 2406,ISO4589 |
|
Water Absorption,%by Volume |
% |
20% |
ASTM C 209 |
|
Dimension Stability |
|
≤5 |
ASTM C534 |
|
Fungi resistance |
- |
Good |
ASTM 21 |
|
Ozone resistance |
Good |
GB/T 7762-1987 |
|
|
Resistance to U.V. and weather |
Good |
ASTM G23 |
|
Advantages of product
Indoor Air Quality-friendly: Fiber-free, formaldehyde-free, low VOCs, non-particulate.
Quiet: vibration damage and Noise blocking.
Durable: No fragile vapor retarder.
The Manufacturing Process of Kingflex Thermal Insulation Rubber Foam Sheet
The three main components used in the manufacturing of elastomeric closed cell foam insulation include the following:
Synthetic rubber blend, typically nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) and/or ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) A chemical foaming agent
These components are combined in a large mixer, typically in batches of 500 pounds or more. The mixture is then put through extruding equipment to form a particular profile or shape, typically either a round tube or a flat sheet. The profile is heated in an oven to a specific temperature, a process that causes the chemical foaming agent to change from a solid to a gas. When this occurs, thousands of tiny air pockets (cells)—all of which are connected—form. The profile is carefully cooled to ensure that these cells remain unbroken and intact, maintaining the material’s closed cell structure. It is then cut to size and packaged for shipment. Elastomeric foams are made without the use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), or hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), making them suitable for the toughest environmental specifications.
Our Company
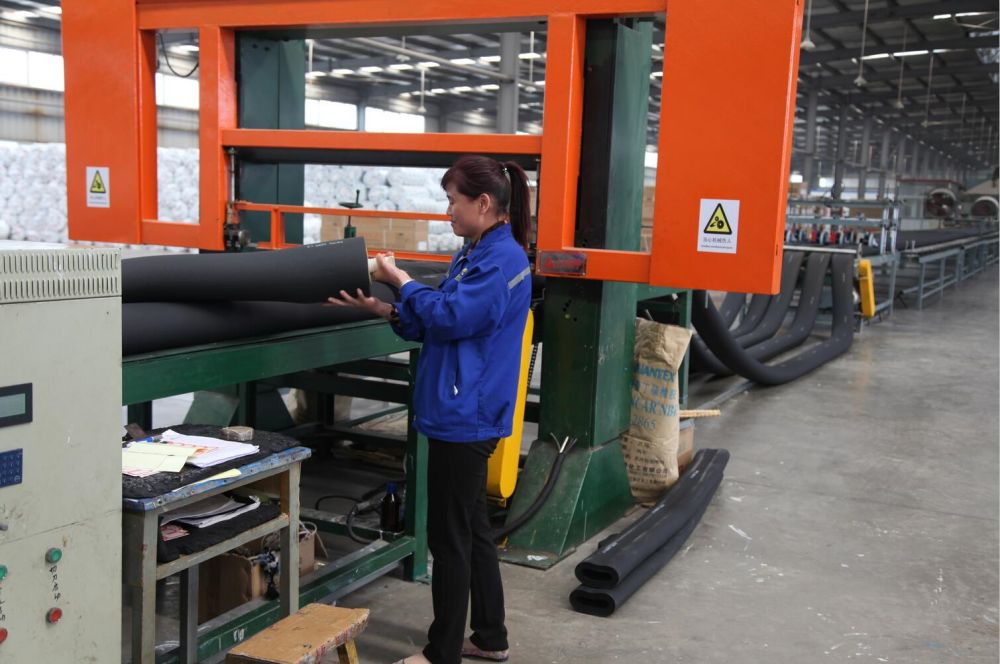




Company exhibition




Certificate



Product categories
-

Phone
-

E-mail
-

Whatsapp








